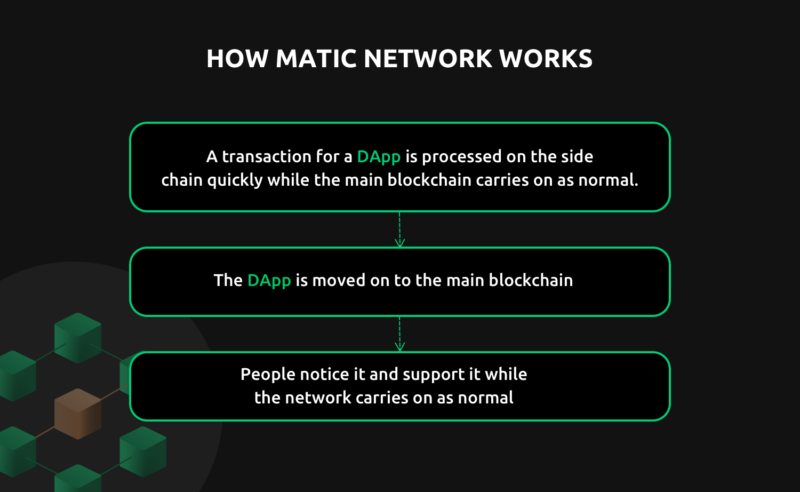
Matic Network (Polygon) is a project that is working to solve the Ethereum blockchain scalability problem.
Polygon solves blockchain-related pain points, such as high gas bills and low speeds, without sacrificing security. This multi-chain system is similar to other systems like Polkadot, Cosmos, Avalanche, but it has at least three main advantages:
1. Can fully benefit from Ethereum’s network effect
2. Is inherently more secure
3. More open and stronger
In this Matic Network review, we’ll take a closer look at the project and answer it. I am looking at their technology, development, roadmap, and long-term potential and use cases of MATIC tokens.
Matic Architecture
Polygon architecture consists of four different layers, each responsible for functions and services used for several purposes.
- Ethereum layer
The Ethereum layer Represent a set of smart contracts implemented on the Ethereum network. They can handle the participation, transaction termination, and communication between various Polygon and Ethereum chains.
- Security layer
The security layer runs with Ethereum. It provides the “Verifier as a Service” function and provides an additional layer of security for the chain.
- Polygon Network layer
The network layer serves as a blockchain network ecosystem built on Polygon. Everyone has their own community and manages production blocks and local consensus.
- Execution layer
The execution layer is represented by Polygon’s Ethereum Virtual Machine Implementation (EVM), which is applied to the execution of smart contracts.
What makes MATIC special?
Matic aims to improve blockchain scaling and interoperability. Several prime features have contributed to the platform’s popularity and hopeful analysts’ outlook:
- Because of its EVM compatibility, Polygon is beneficial to anyone developing applications on Ethereum and programs in Solidity.
- A Matic security model is optional – there’s no need to sacrifice flexibility for the sake of additional security if not needed.
- Polygon claims to have sufficient flexibility to incorporate various scalability solutions outside of the Plasma Chain, such as optimistic rollups or ZKrollups.
 MATIC Technical Analysis
MATIC Technical Analysis
MATIC tokens in the Polygon ecosystem are used for a variety of purposes, including payment of gas charges and security contributions through staking. It is one of the 20 most flexible and biggest coins by market capitalization (September 4, 2021).
Guessing about the MATIC coin forecast, it is worth mentioning that competition is ongoing for the most important interoperability solutions. Polygon rivals Polkadot and Cosmos’ Stargate are also launching solutions.
MATIC is one of the most promising password coins of the year. From the beginning of 2021, the price was $ 0.01 on January 1, 2021, and surged to the current level of $ 1.65 (Sep 4). This nearly 16,300% increase seems to support the claim for high MATIC coin price forecasts.
Also Read: Polkadot (DOT)
MATIC Network Goals
In extension to solving scalability issues, the Matic Network focuses on improving usability without losing the benefits of decentralization. The founders of the Matic Network found that despite the large number of proposals and developments for dApps, the running network was unprepared to support the mass adoption of dApps. Also, in many cases, the user experience is poor. dApps are not friendly to the general public.
The first blockchain was to highlight the potential of the Matic is Ethereum. The developers have started implementing their work on the Kovan testnet. It is a modified version of the Plasma network, but eventually, the Matic development team envisions using it as a side chain extension solution for all blockchains.
The 2019 team was able to release Alpha Mainnet for the first time in June. This net was the first Matic side chain to run on the Ethereum mainnet, allowing developers to build and test dApps. Still, it wasn’t the last. The beta mainnet was also mobile in September. It included new features such as Heimdall, Bor, Plasma conditions, and more.
Addressing Blockchain Challenges
Despite how advanced blockchain technology has become, there are still several problems that they face. In some cases, trying to improve on a challenge can result in the potential sacrifice of other functions.
Scalability
Scalability can achieve by adding new side chains horizontal, with each side chain. In theory, using the same proof-of-stake checkpoint layer increases capacity to 216,216 transactions per second.
It gives the Matic Network the power to scale to many transactions per second.
Size of Blockchain
since the public chain requires each node to manage a full copy of the block and the state of the chain, as time goes by, the blockchain gets bigger and the number of participating node decrease, which is the decentralization of the blockchain.
For Matic networks, the main tier can only store blocks from the last checkpoint to the latest checkpoint. you can do this because all the previous blocks have been committed to the main chain. This even allows mobile devices to run nodes.
Slow Transactions
In most cases, blockchain transactions are slow, especially when testing the blockchain. Matic then uses the proof of stake as the Merkel root layer that verifies the block and publishes the side chain block on the Ethereum main chain. It enables Matic Network to keep the block confirmation time below 2 seconds while providing a high degree of decentralization.
High Transaction Fees
The block size of most blockchains is limited, leading to changes in fees based on groups of pending transactions. In some cases, the cost becomes very high over a period of time.
Matic can take advantage of economies of scale by completing a large number of transactions on the Block Producer layer. This keeps the cost of each transaction low.
Poor Usability
Compared to the established centralized counterpart, the dApp user interface is poor. The Matic team is creating web and mobile browser integrations and protocols to improve the usability of dApps in a secure interactive environment.
Multiple micropayment channels with other off-chain solutions
Solving the problem of opening multiple channels to enable small payments is complex and we have proposed solutions for multiple projects. The Matic network solves this problem using the Ethereum virtual machine, without opening payment channels for micropayments.
In contrast, any valid Ethereum address is also a valid Matic address, which means that no recipient needs to be on the Matic network. They only need a Matic wallet to retrieve payments.
The MATIC Wallet
This wallet helps users with Dapps to interact with ethereum and plasma chains. wallets significantly increase the trading speed by allowing access to two different networks at the same time.
In addition, it allows the connection of the DAPS desktops with mobile forest bearings with simple end-to-end encryption when the QR code scans. This allows users to interact with DAPPS without separate buttons from their devices.
It is still in the testing phase. The team warns everyone not to send mainnet tokens to the wallet, otherwise, they will be lost. Anyone downloading the wallet now, regardless of the Android or iOS version, will receive MATIC test tokens.
MATIC Dagger
Another very interesting product in the Matic suite is Dagger. This is the infrastructure that offers reliable and scalable real-time events. It can be thought of as similar to an off-chain solution, where the necessary information in the DAPP comes from.
The cool thing about Daga is that it can be easily integrated with your current DAPP. Obtaining any event stream from the Ethereum blockchain requires only a few lines of code.
Dagger can also help you interact with users when they are offline. Basically, you can listen to specific user events 24/7. Once these events occur, you can send email or DM notifications to make the application easier to use.
MATIC Network Team
The Matic Network team consists of three co-founders, eight engineers, a chief operating officer, and a community manager. The project also added a pair of vice presidents of operations and marketing last year, a vice president of finance and operations, and several chief designers focused on design.

Matic Network also cooperates with several major blockchain projects, including MakerDao and Decentraland. In addition, Ari Meilich and Esteban Ordano, CEO and CTO of Decentraland, acted as consultants for the project.
MATIC Marketing and Social Networks
Although Matic has a group of excellent partners and consultants, it is worth noting that they have been selected to launch their ICO on the Binance Launchpad platform, but their performance on social media is very poor.
In the 28 months since April 2019, the number of followers on the Twitter account has increased to 636k, when there were only 2351 followers.
Matic also has a medium blog, which was pre-updated every month or every few weeks. It has been updated more frequently, and the team has kept the community abreast of the latest developments in the project. They have a Telegram channel with more than 56,000 members.
Overall, the social influence of the Matic Network has grown tremendously in 2019, highlighting the power of people to support the project.
MATIC Network Strengths
one of the strengths of this project is a large number of use cases available. These include decentralized transactions, identity features, credit ratings, atomic transactions, payment, and gaming networks.
One of the features that Matic is developing is Zappier integration through Dagge. It allows developers to connect Ethereum platforms with hundreds of applications and to help boost user and developer adoption.
Conclusion
Matic is a protocol and framework for building and connecting an Ethereum-compatible blockchain network.
- One-click implementation of pre-established blockchain networks.
- The modules used to develop custom networks are constantly increasing.
- They need an Interoperability protocol used to exchange arbitrary messages with Ethereum and other blockchain networks.
- Optional modularity and security as a service.
- The adapter module is used to realize the interoperability of the existing blockchain.






 MATIC Technical Analysis
MATIC Technical Analysis